In the dynamic world of cloud infrastructure, changes are constant. Every modification, no matter how small, can have a significant impact on the performance and security of your cloud environment. Keeping on top of changes as they happen puts you ahead of the game. This is where Hava.io, with its versioning and historical data features, comes into play.
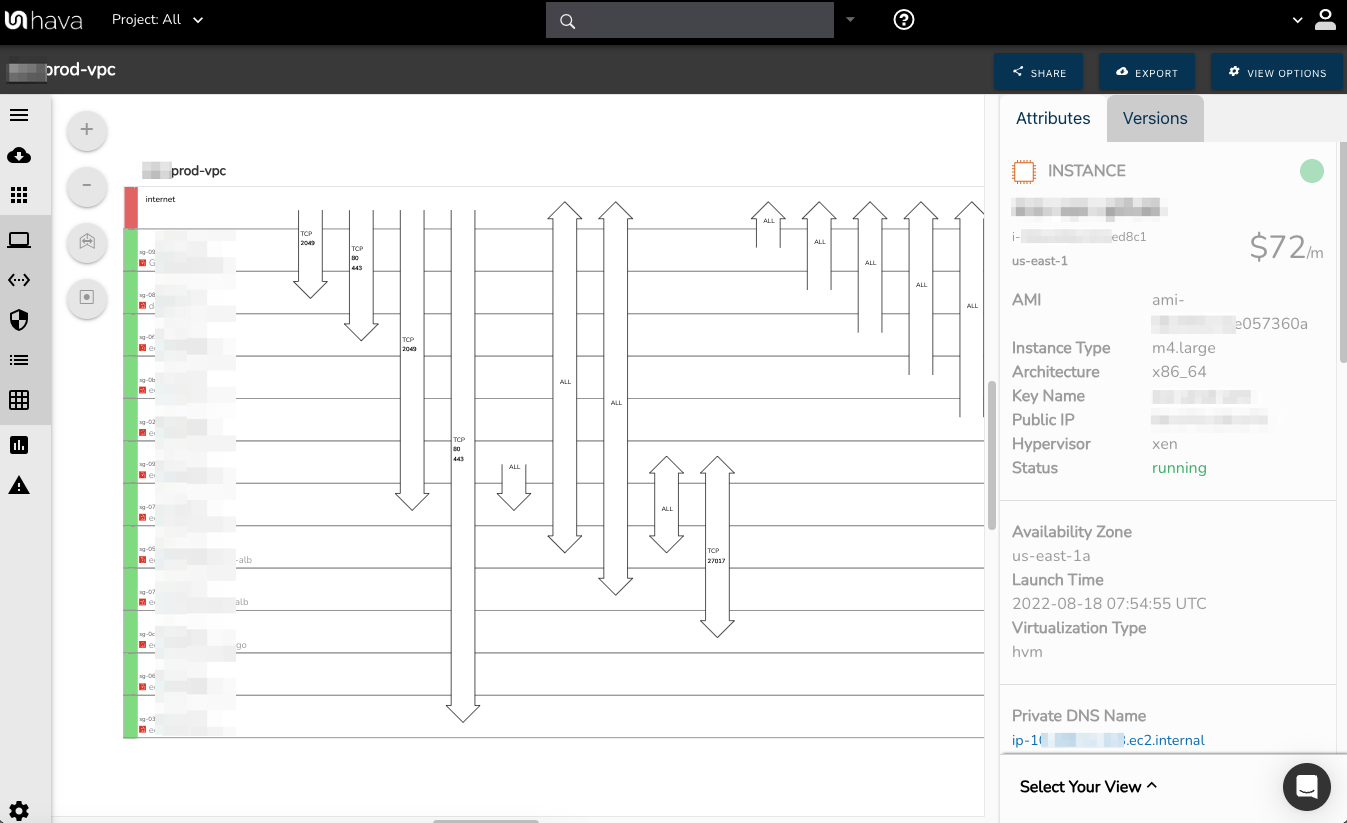
Hava.io is a software platform that automatically diagrams and monitors the cloud infrastructure of connected Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Azure accounts. One of its key features is the ability to track changes over time and provide a historical view of your infrastructure.
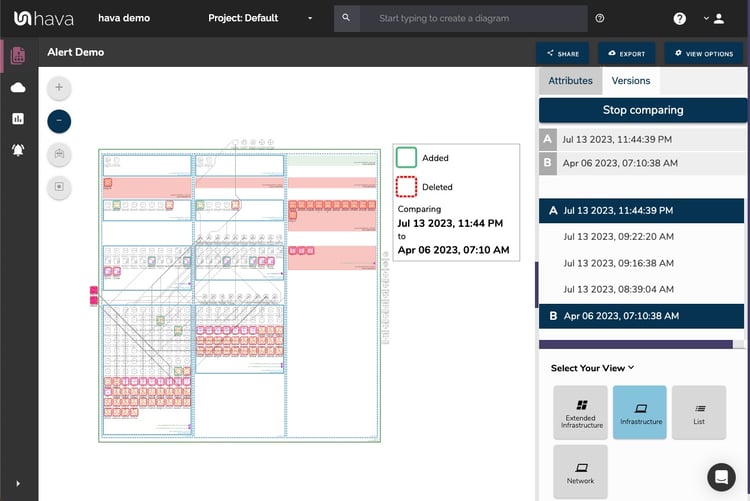
When Hava.io detects a change in your cloud environment, it automatically generates a new diagram and moves the old one to versioning. This means that you always have an up-to-date view of your infrastructure, but you also have access to a historical record of how your infrastructure has evolved over time.
This feature can be invaluable when troubleshooting issues. Often, problems in cloud infrastructure are not the result of a single change, but the cumulative effect of multiple changes over time. With Hava.io's versioning and historical data, you can trace back the changes to identify when and where the problem started.
Moreover, having a historical view of your infrastructure can also help in planning future changes. By understanding how your infrastructure has evolved and how changes have impacted performance and security, you can make more informed decisions about future modifications.
Hava.io's versioning and historical data features are powerful tools for cloud infrastructure troubleshooting. They provide a clear view of how your infrastructure has evolved over time, helping you identify the root cause of problems and plan future changes more effectively.
To learn more about how Hava.io can aid in troubleshooting and maintenance of your cloud infrastructure, check out this detailed post.

Or you can hop straight into a 14 day free trial here:
(no cc required)