AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials | Global Infrastructure and Reliability
AWS Global Infrastructure and Reliability is a topic covered in AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials. In this post we take a look at what makes up the...

AWS cloud WAN allows you to connect your on premise networks at your company locations, data centers and AWS VPCs together using the AWS global network backbone without having to use the internet.
Using the network manager console, with just a few clicks, you can connect offices together, create connections to your AWS VPCs running in the cloud and connect to assets and servers colocated in data centers.
Cloud WAN generates a complete view of your entire on-cloud / off-cloud networks to help monitor network performance, health and security.
Traditionally it would take a significant amount of time to build a wide area network especially where the network was distributed across different continents and subject to multiple telecommunications providers with multiple comms speeds and protocols. Sourcing and configuring network equipment like routers and switches and securely configuring them so your offices and/or departments can share data, access centralised applications or databases was a lengthy and highly technical undertaking.
Using Cloud WAN you connect to AWS via a choice of local network providers (not the internet) and then using the dashboard you can create a unified network that connects your branch office locations, AWS VPCs and transit gateways, VPN connections, SD-WANs and data centers in a matter of minutes.
The central dashboard allows you to simplify set up and day to day operations of potentially complex large global networks, reducing previously time consuming and complex on prem network configuration challenges down to a few clicks.
The centralized nature of Cloud WAN means you can define global access controls and routing in one central networking policy document. To avoid inadvertent negative impact on your global network, when you make changes to a policy, you need to review and validate the changes are working as expected and then approve them for roll out. Cloud WAN then handles the configuration changes across your entire network.
Policy amendments can be made using the AWS network management console or programmatically using the Cloud WAN APIs
Attachments can be used to get Cloud WAN to segment your network traffic no matter how many AWS regions or on prem locations you add to the network. You can for instance isolate the IT department from accounting, but still give each shared access to some corporate resources. This centralised approach makes it easier to apply a uniform set of security measures across multiple locations, business units and AWS resources while Cloud WAN ensures a consistent configuration is applied across all the regions you have resources running in.
Cloud WAN can also automatically attach new VPCs and network connections to your network as they are created by tagging attachments with a tag that relates to a specific network segment. You can choose to let specific tags dictate automatic addition to the network so you don’t need to approve the addition to the network, or you can define an attachment tag as requiring manual approval. You can also specify if new attachments on the same network segment can communicate with each other based on the tag.
A traditional WAN for a globally distributed network can be hard to to set up and manage. Adding a new node for a branch office or new country can take weeks or months to complete successfully, and of course sorting out the security, separate firewalls and peering connections between the existing network components can be quite challenging.
Add to that the need to provide VPN access for modern work-from-home requirements and the complexity and required security escalates.
Traditional Wide Area Network (Legacy WAN)
Up until quite recently, a corporate WAN generally serviced users in specific company locations with the internal network traffic routed through hardware to access applications in data centers and shared files and databases in other company locations. Connections were typically VPN tunnels or hard MPLS connections provided by a telco. Commissioning a new location could take weeks or even months to source and commission the required hardware and comms connections. Once multiple branch offices in disparate geographic locations are in play, it doesn’t take long for the required connectivity and security to become problematic.
Once cloud is adopted in conjunction with the corporate WAN, another layer of connectivity is introduced, which is the same for the adoption of SD-WAN technology and with the current somewhat enforced trend of remote workforces secure client VPN connections are also added to the mix. Inevitably you end up with mismatched firewalls, connectivity and access issues, in a nutshell complex WANs are hard work.
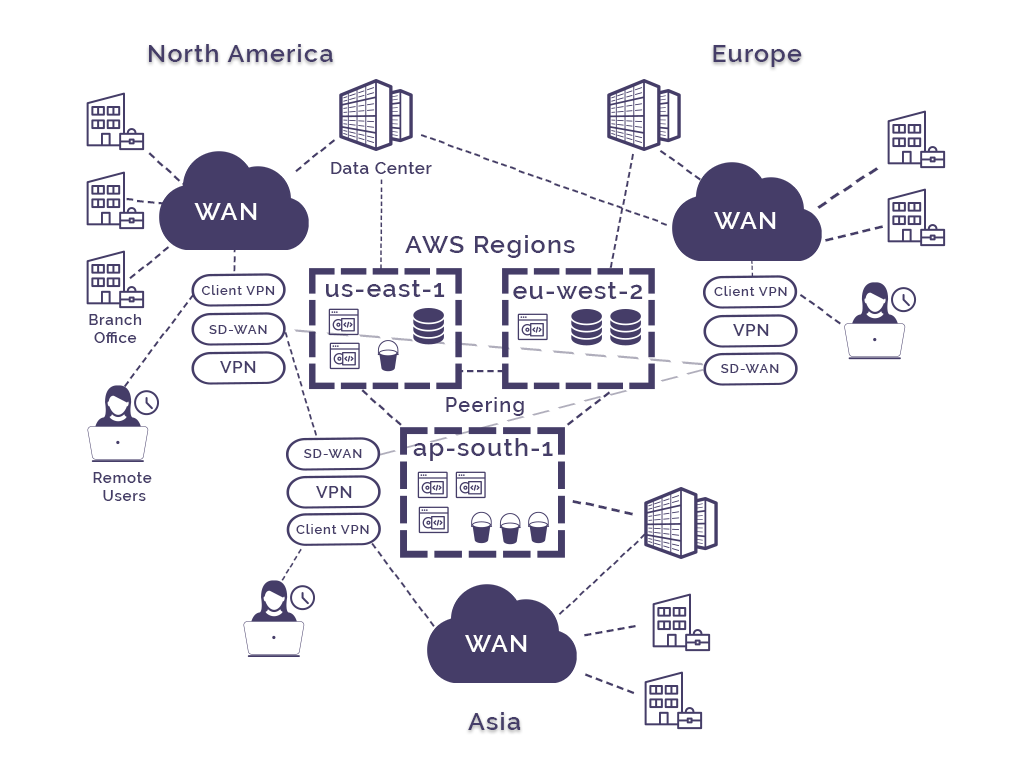
AWS Cloud WAN was built to simplify the process and allow you to build global network that integrate with your AWS infrastructure in minutes using the AWS global backbone.
Cloud WAN simplifies your WAN networking and allows you to segment traffic with a centralized permissions policy governing which segments of your core network can see attached resources.
The service allows you to utilise your existing infrastructure at your company locations and connect your VPCs, SD-WANs, Client VPN, Firewalls, VPNs and data center resources to connect to Cloud WAN.
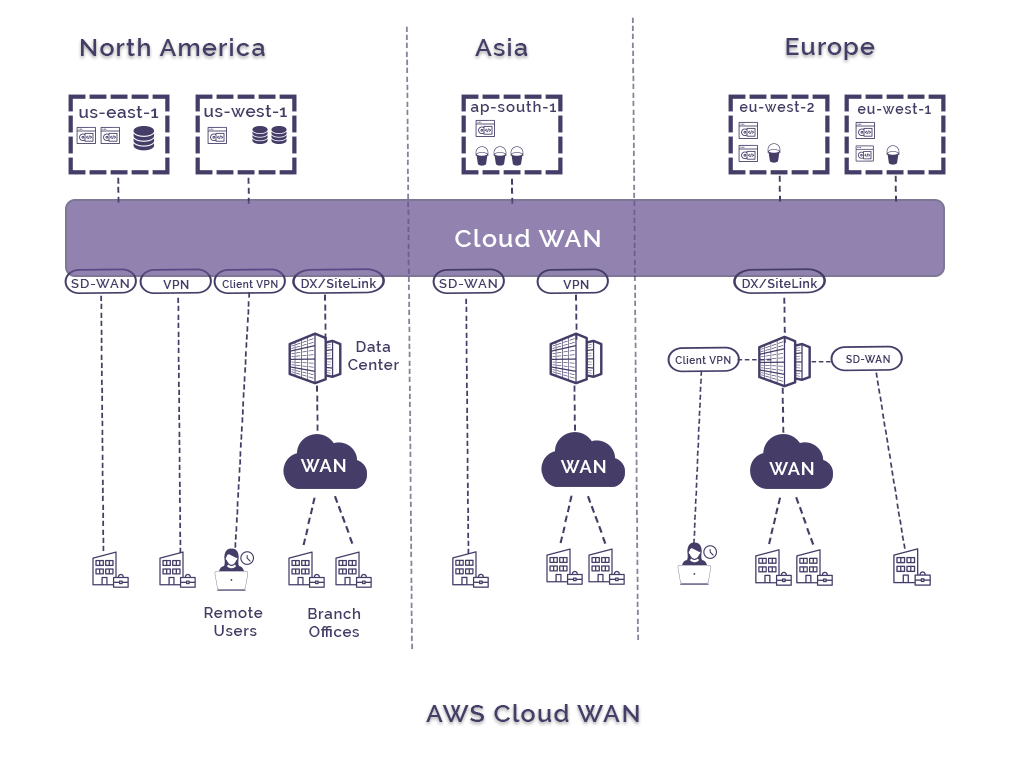
Wide Area Network.
Even if you are not hosting data or running workloads in VPCs, you can use AWS Cloud WAN to set up a wide area network over the AWS global backbone. You are able to use existing router to firewall connections and use VPN, SD-WAN, Client VPN or direct connect to connect your locations to AWS Cloud WAN.
This then allows you to control access via a central policy and add new locations to your WAN in minutes.
If you don’t care about access to cloud resources and just want to connect port-to-port then direct connect site-link is possibly an easier option.
Global VPC
One of the challenges when you have multiple or maybe hundreds of VPCs running on AWS across multiple regions and availability zones is granting access between VPCs.
This is traditionally done using static route tables.
Cloud WAN removes this administrative nightmare by automating the process from a centrally managed policy.
The cloud WAN can also be segmented. If you have different business units, different companies or want to reserve a space for developers or contractors away from your production environments, you can use cloud WAN to segment.
The Global Network is a pre-existing construct built in to AWS Network Manager that is leveraged to set up Cloud WAN.
Within Global Network you define a Core Network that holds what is going to be controlled by the Cloud WAN instance as dictated by the core policy.
Within the core you create segments like Development, Production, Contractors etc and then create attachments or respond to attachment requests. Attachments are things like VPNs, direct connect or site-link connections and VPCs.
To manage the WAN you create a Core Network Policy that governs how the entire global network behaves. AWS will then create core network edge instances in each region which are similar to transit gateways which enables BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) which provides fully managed dynamic routing across the WAN.
Attachment policies govern what happens when an attachment request is received.
A VPC owner can raise an attachment request and can tag the request. The tag could be something like “environment:development”
The Cloud WAN administrator can set up policy rules that tell Cloud WAN what to do when the attachment request is received. So in this instance you might have a rule that says when the request is tagged “environment:development” then automatically attach the VPC to the Development segment, at which time the VPC will become visible in that segment.
Other metadata can also be used within the policy as attachment condition options such as resource ID, resource type, region, account ID or resource tag values.
The attachment tag is not the same as the normal VPC tags.
An example of the steps you would take to implement Cloud WAN would be :
When you create a network policy, when you submit it, AWS will analyse it and create a list of all the changes it will make. You can then review the changes or submit them to others within your organisation for approval. Once approved you then approve the changes and AWS Cloud WAN makes them live.
So that’s an AWS Cloud WAN brief intro.
If you are building networks or applications on AWS you can use Hava to produce hands-free AWS network topology diagrams (oh, Azure and GCP are also supported).
You can get a free 14 day trial, learn more using the button below:
AWS Global Infrastructure and Reliability is a topic covered in AWS Cloud Practitioner Essentials. In this post we take a look at what makes up the...
AWS VPC Peering connections lets a VPC communicate with resources in another VPC. The target VPC can be in your account, in a different region or in...
The Hava AWS Diagram tool is the easiest way to automatically create interactive AWS Cloud diagrams that detail regions used in your VPCs